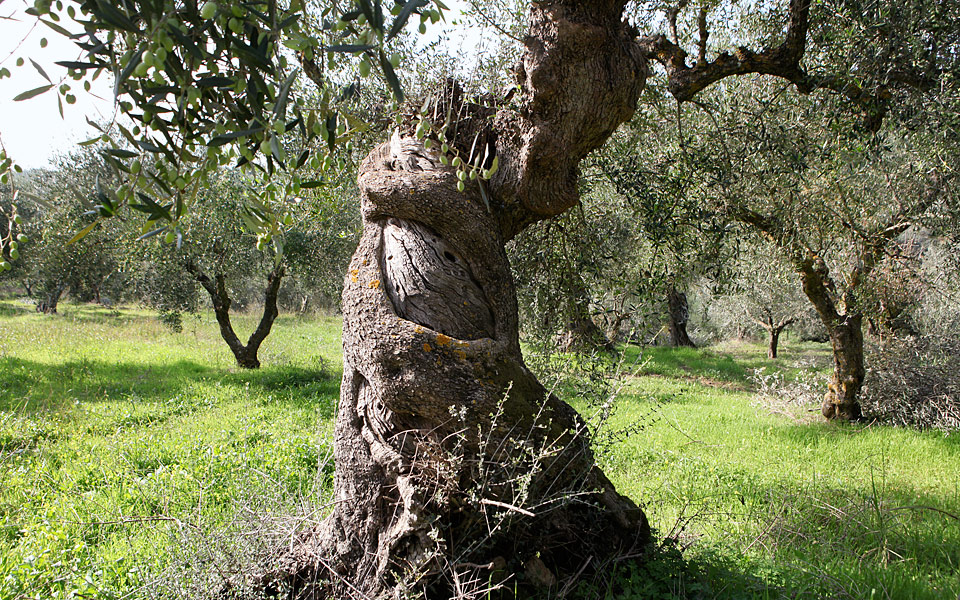
The presence of the olive in Greece has been documented since the Neolithic age.
The ancient Greeks loved the olive and ascribed it divine origins. A typical instance is the well-known myth of Poseidon and Athena’s contest over the name of Athens.
For Homer, olive oil was “liquid gold.” In ancient Greece the olive held an important place both in the nutrition of citizens and in the city’s economy. In “Oedipus at Colonus” Sophocles calls the olive “nurturer of children.” It was a symbol of peace and whoever offered an olive branch was received with respect. An olive branch was also the prize awarded the winners at games. In the Panathenaic Games the winner of the footrace received as a prize 700 amphorae of top-quality oil (which must have corresponded to about 2.5 tons) and the winner of the chariot race received approximately 5 tons. The athletes usually sold the oil, and the amphorae, outside Athens.
Apart from food, olive oil was also used as a basic ingredient in the cosmetics and perfume industry and as fuel for lamps. This usage still survives in the small devotional oil lamps (kandilia) used in churches and household shrines.
For Homer, olive oil was “liquid gold.” In ancient Greece the olive held an important place both in the nutrition of citizens and in the city’s economy.

© Katerina Kampiti
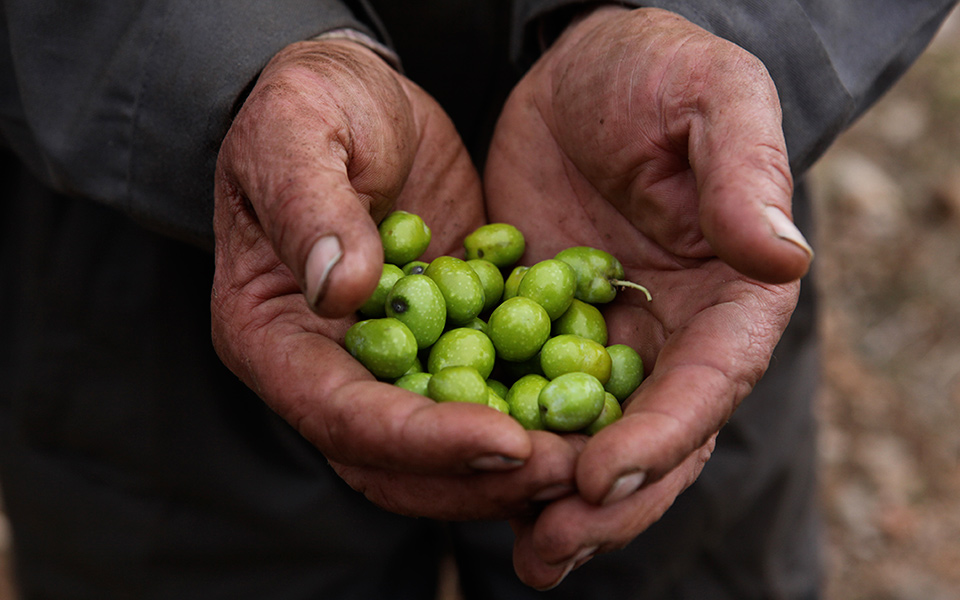
“Some methods used by the
ancient Greeks are still
practiced today. After
soaking olives in brine
to get rid of the bitter taste,
they soaked them
in vinegar for a few hours
and finally stored them
in olive oil.”
There was a great variety of edible olives, as attested in ancient authors. Kolymbades and almades were olives cured and preserved in brine. Hermippus mentions that “in the olives swimming in brine we add fennel.” “Thlastai elaiai” were cracked olives. Large spherical olives were called “gongylai” and very mature, wrinkled ones were called “drypeteis.” “Pityrides” were small olives the color of oats. “Stemphylides” were black and were ground into a paste called “stemphylon,” which was seasoned with herbs, oil and vinegar (just as we do now) to make a tapenade called “epityron” that was eaten with cheese.
Some methods used by the ancient Greeks are still practiced today. After soaking olives in brine to get rid of the bitter taste, they soaked them in vinegar for a few hours and finally stored them in olive oil. One author recommends a gourmet recipe: preserve the olives in vinegar that has been boiled with wine and spices such as coriander, cumin, fennel and mint.
Pliny also recommended adding aromatic herbs to olive oil. And since some things in Greece remain unchanged through the centuries, Clearchus, the peripatetic philosopher, gives the following instructions for frying the small tasty picarel fish: it should be fried on a low fire because it cooks quickly; the friends of Archestratus (that was what gourmands were called at the time) heated the oil well in the pan and remove the picarel as soon as it is cooked.